Match Each Embryonic Membrane With Its Function.
The central vacuole of plant cells and fungi has a homeostatic function ensuring cell turgor and its membrane the tonoplast has ion pumps. Mucosae is a layer of cells that surrounds body organs and body orifices.

Embryonic Fetal Development Human Embryo Fetal Development Fetal
Ectoderm and somatic mesoderm surrounding the embryo form a protective covering over the embryo called the amnion.

. Evolution of eggs with a water-impermeable amniotic membrane surrounding a fluid-filled amniotic cavity permits embryonic development on land without danger of dessication. Cover organs in closed body cavities. Match each embryonic membrane with its function.
Each of these lineages of embryonic cells forms the distinct germ layers from which all the tissues and organs of the human body eventually form. Surrounded by amniotic fluid the embryo is kept as moist as a fish embryo in a pond. Match each embryonic membrane with its function.
Match each epithelial membrane with its proper locations and functions. The main diagram shows the arrangement of membranes in a typical egg-laying oviparous vertebrates. Explain how an embryo transforms from a flat disc of cells into a three-dimensional shape.
Encloses the embryo and filled with protective fluid. The third membrane is the allantois which forms as a small pouch at the posterior tail end of the embryo. The amnion yolk sac allantois and chorion.
Some central vacuoles are also sites of accumulation of reserves or of particular substances sometimes toxic latex. The amount of amniotic fluid then declines to 5001000 ml near the time of birth. Packaging center Lcytoplasm D.
Amnion- Encloses the embryo and filled with protective fluid. Produces proteins lysosome B. Mucous membranes can contain or secrete mucus which is a thick fluid that protects the inside of the body from dirt and pathogens such as viruses and bacteria.
Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and. Line closed body cavities. It is made from ectodermal tissue.
Contributes to the formation of the digestive tract. Allantois Amnion Yolk sac Chorion 1. Distinguish the stages of embryonic development that occur before implantation.
The inner layer of cells secretes amniotic fluid in which the embryo floats. A mucous membrane also known as a mucosa plural. The third membrane is the allantois which forms as a small pouch at the posterior tail end of the embryo.
Yolk sac- Contributes to the formation of the digestive tract. V It permits foetal movement. There are four layers.
Encloses the embryo and filled with protective fluid Contributes to the formation of the digestive tract Becomes part of the urinary bladder Eventually forms the fetal portion of the placenta. It also absorbs the dissolved yolk and passes it to developing embryo. Although most mammals do not make a shelled egg they do also enclose their embryo in an amnion.
Third draw in arrows and color them to match each of the coding circles associated with the conditions noted just below. Larger size in plant cells is matched with vacuole. Extraembryonic membranes are the layers enclosing the embryo inside the uterus.
Embryonic cells that have the ability to differentiate into any type of. Although it has important functions in waste storage. Describe the process of implantation.
Gel like substance that protects organelles cell membrane E. In human beings it is vestigial. Breaks down food and worn out cell parts 3D Lvacuole F.
1 Match each embryonic. Epithelial tissue connective tissue muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Match the organelle to its function.
See-through cells plasma membrane to indicate its electrical polarity. Ii It cushions the embryo protecting it against bumps and pressure of the maternal organs. Structure and Functions Figure 31 is a diagram of a portion of a plasma membrane.
This fluid keeps the embryo from drying out and helps protect it when the egg is jarred. Iii It maintains constant temperature and pressure. The amount of amniotic fluid then declines to 5001000 ml near the time of birth.
Contributes to the formation of the digestive tract. Controls what passes into and out of the cell iribosome C. Thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body organs and internal cavities.
Match each element with its important function. Describe how the placenta is formed and identify its functions. A tissue is a group of cells in close proximity organized to perform one or more specific functions.
Write the letter of the correct answer in the blank. Ectoderm Ecto- outer mesoderm Meso- middle and endoderm endo- inner. Absorb x-rays in bones sodium 3.
Group of cells that are similar in form and perform related functions. In live-bearing viviparous vertebrates the shell and chorionic membrane. Connects to the ER.
Line the respiratory and digestive tracts. Break down of food into energy calcium 2. Secrete serous fluid to prevent friction.
A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that either covers the outside of the body eg skin lines an internal body cavity eg peritoneal cavity lines a vessel eg blood vessel or lines a movable joint cavity eg synovial joint. Shows the types of tissues and organs. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Chorion- Eventually forms the fetal portion of the placenta. Match each embryonic membrane with its function. Line the urinary and reproductive tracts.
Two basic types of tissue membranes are recognized based on the primary tissue type composing each. By the end of the embryonic period the embryo is approximately 3 cm 12 in from crown to rump and weighs approximately 8 g 025 oz. It is mainly digestive in function so acts as extra embryonic gut.
Encloses the embryo and filled with protective fluid. It contains water carbohydrates organic and inorganic ions and pigments. Each germ layer is identified by its relative position.
1 Match each embryonic membrane with its function Allantois 2 Chorion لیا Amnion 2013028 Yolk sac Match each of the options above to the items below. Select four differ-. Although it has important functions in waste storage.
An embryo at the end of 7 weeks of development is only 10 mm in length but its developing eyes limb buds and tail are already visible. I Prevents drying of the embryo. Amniotic fluid is secreted and absorbed rapidly at a maximum rate of about 300600 ml per hour.
The amniotic fluid performs many important functions. Iv It prevents bacterial infections. Structure of the Amniotic Egg.
With these four membranes the developing embryo is able to carry on essential metabolism while sealed within the egg. It is formed of splanchnopleur inner endoderm and outer mesoderm and is well developed in reptiles birds and prototherians having poly lecithal egg. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function.
Allantois- Becomes part of the urinary bladder. Made of simple squamous epithelium. Match each embryonic membrane with its function.
List and describe four embryonic membranes. Match each embryonic membrane with its function. Figure 28212 Embryo at 7 Weeks.
Amniotic fluid is secreted and absorbed rapidly at a maximum rate of about 300600 ml per hour. Match each embryonic membrane with its function.
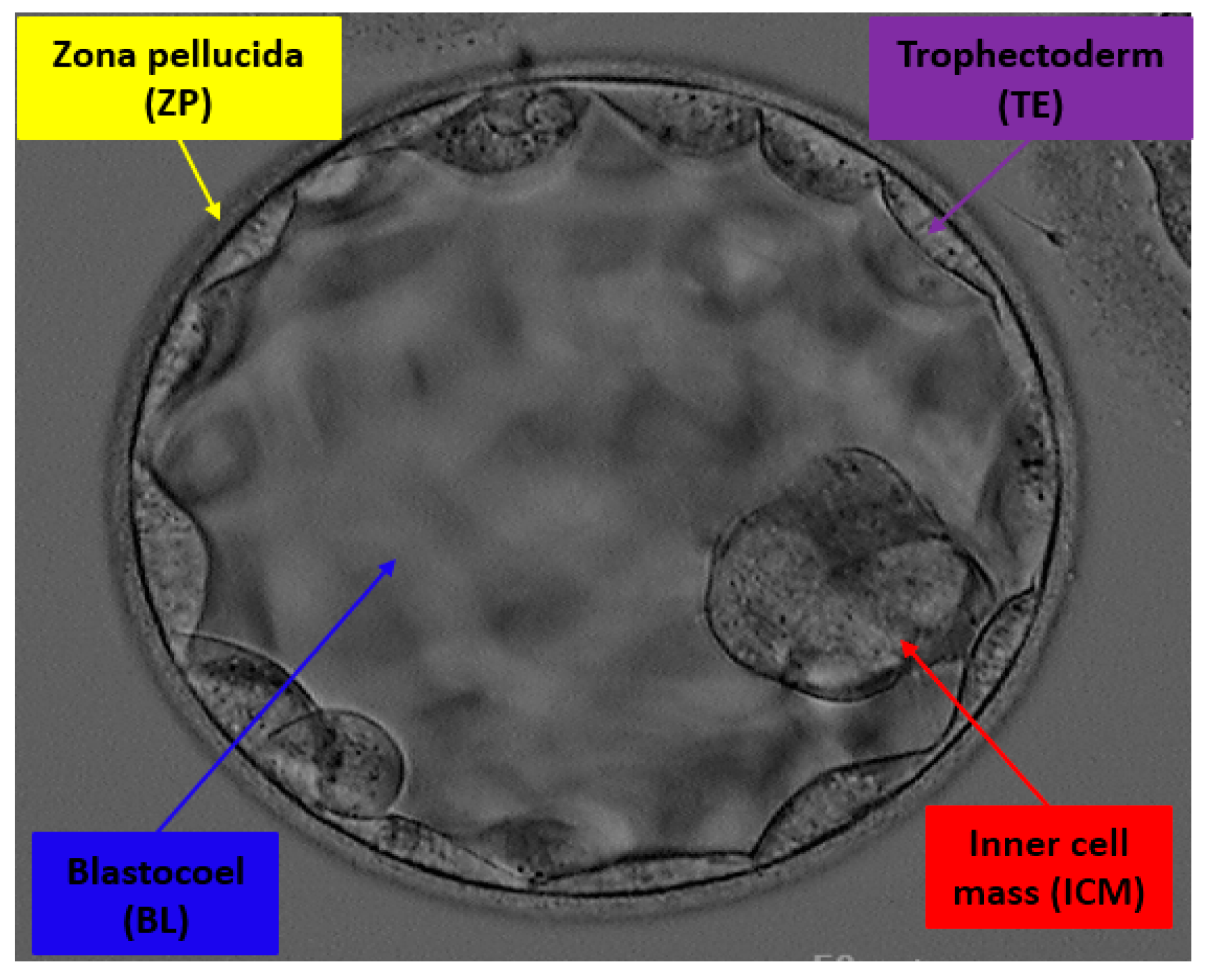
Jpm Free Full Text Detecting Blastocyst Components By Artificial Intelligence For Human Embryological Analysis To Improve Success Rate Of In Vitro Fertilization Html

Biological Basis Of Heredity Cell Reproduction Heredity Meiosis Reproductive System

Unicellular Microorganisms And Their Organelles Human Body Anatomy Organelles Body Anatomy

Year Long Biology Readings And Guided Notes Guided Notes High School Lesson Plans Biology

Embryo Human And Animal Britannica

Strategy For Therapeutic Cloning And Tissue Engineering Tissue Engineering Somatic Cell Renal Cell

Eye Ball Anatomy 1000 Images About Eyeball On Pinterest Ha Definition Human Eye Eye Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Eye Anatomy Diagram

Early Human Embryonic Development Blastocyst Formation To Gastrulation Sciencedirect
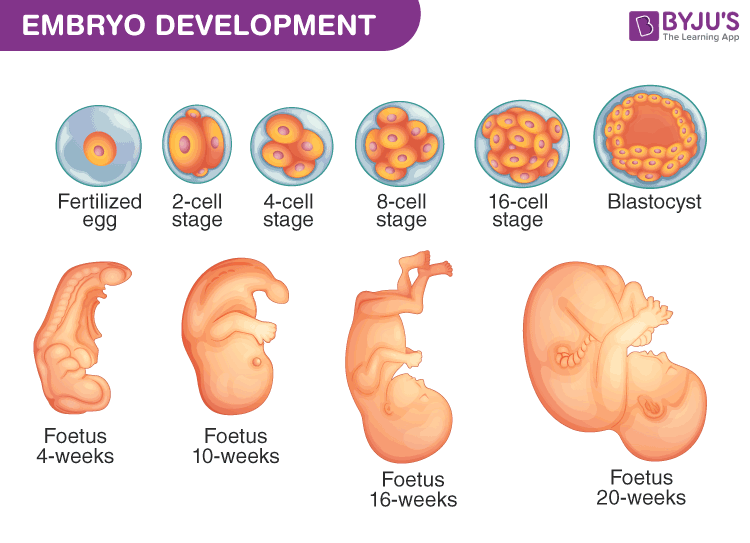
Embryo Development A Development Process Of Fetus Week By Week

12 Differences Between Pollination And Fertilization Pollination Fertility Fertilization Process

Meiosis And Mitosis Teaching Ideas Blog By Science With Mrs Lau Biology Worksheet Mitosis Cells Worksheet

Sci Ence Embryo Comic By Maki Naro

Apple Seed Anatomy Apple Seeds Apple Tree Seeds

Design A Playground Assignment Child Development Education Training Family And Consumer Science Child Development Teaching Child Development Activities

Copyright C 2008 Pearson Education Inc Publishing As Pearson Benjamin Cummings Powerpoint Lecture Presentations For Biol Pearson Education Biology Lecture
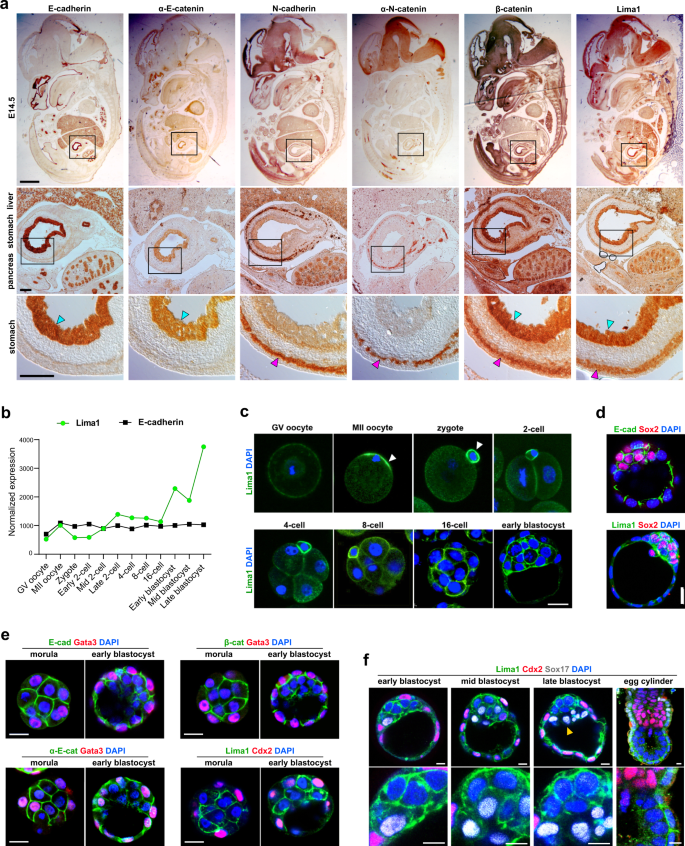
Lima1 Mediates The Pluripotency Control Of Membrane Dynamics And Cellular Metabolism Nature Communications

Harga Mac Pro Dan Layanan Upgrade Hardware Sekarang Turun Cek Disini Harganya Http Situsiphone Com Harga Mac Pro Dan Layanan Upgrade Mac Pro Pelayan Mac

Animated Virtual Trading Cards That Show Off The Fascinating Molecular Structure Of Individual Viruse Science Infographics Infographic Illustration Infographic

Comments
Post a Comment